Your First App
Work in Progress!
We're actively working on finishing up the Syncbase API and implementation. The code below compiles, but may not execute successfully. Please join our mailing list for updates.
Introduction
In this quick tutorial, we will build a Dice Roller Android app where one can simply generate a random number between 1-6 and have it sync across multiple devices peer-to-peer, even with Wi-Fi turned off!

Setup
This tutorial uses Android Studio, but feel free to use your IDE of choice.
Create the Project
We will start by creating an empty project in Android Studio
File -> New -> Project.
Select API 21 or above for the Minimum SDK and pick Empty Activity as the
template.
Install Syncbase
Add the following to your build.gradle file.
cat - <<EOF >> $PROJECT_DIR/app/build.gradle
dependencies {
compile 'io.v:syncbase:0.1.7'
}
EOF
Setup Cloud Syncbase
Head to https://sb-allocator.v.io/ to setup a free developer cloud Syncbase instance or access your existing one.
Make note of the Syncbase Address and the Blessing for your cloud instance, they are required by the Syncbase API during initialization.
Note
Requiring a cloud Syncbase is temporary. We are planning to allow the API to be used without a cloud Syncbase very soon.
Initialize Syncbase
MainActivity.java
cat - <<EOF | sed 's///' > $PROJECT_DIR/app/src/main/java/io/v/syncbase/example/MainActivity.java
{#dim}{#dim-children}package io.v.syncbase.example;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;{/dim-children}{/dim}
import io.v.syncbase.Syncbase;
import io.v.syncbase.exception.SyncbaseException;
{#dim}{#dim-children}public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "DiceRoller";
// Note: You can replace CLOUD_NAME and CLOUD_ADMIN with your cloud syncbase
// name and blessing from https://sb-allocator.v.io
private static final String CLOUD_NAME =
"/(dev.v.io:r:vprod:service:mounttabled)@ns.dev.v.io:8101/sb/syncbased-24204641";
private static final String CLOUD_ADMIN = "dev.v.io:r:allocator:us:x:syncbased-24204641";
private static final String MOUNT_POINT = "/ns.dev.v.io:8101/tmp/diceroller/users";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);{/dim-children}{/dim}
try {
String rootDir = getDir("syncbase", Context.MODE_PRIVATE).getAbsolutePath();
Syncbase.Options options =
Syncbase.Options.cloudBuilder(rootDir, CLOUD_NAME, CLOUD_ADMIN)
.setMountPoint(MOUNT_POINT).build();
Syncbase.init(options);
} catch (SyncbaseException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Syncbase failed to initialize", e);
}
Syncbase.loginAndroid(this, new LoginCallback());
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
Syncbase.shutdown();
super.onDestroy();
}
private class LoginCallback implements Syncbase.LoginCallback {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Syncbase is ready");
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Syncbased failed to login", e);
}
}
{#dim}{#dim-children}}{/dim-children}{/dim}
EOF
Now, let's run the app to make sure login and Syncbase initialization are working.
After running, you should see Syncbase is ready in logcat under Android Monitor
or in the console.
UI Code
The user interface is just a TextView to display the dice roll
result and a Buttons to roll the dice.
Here is the UI code
activity_main.xml
cat - <<EOF | sed 's///' > $PROJECT_DIR/app/src/main/res/layout/activity_main.xml
{#dim}{#dim-children}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="io.v.syncbase.example.MainActivity">{/dim-children}{/dim}
<TextView
{#dim}{#dim-children} android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"{/dim-children}{/dim}
android:text="Dice Not Rolled yet"
android:id="@+id/textViewResult"
{#dim}{#dim-children} android:layout_marginTop="36dp"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />{/dim-children}{/dim}
<Button
{#dim}{#dim-children} style="?android:attr/buttonStyleSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"{/dim-children}{/dim}
android:text="Roll the Dice!"
android:id="@+id/buttonRoll"
{#dim}{#dim-children} android:layout_marginTop="40dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/textViewResult"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
</RelativeLayout>{/dim-children}{/dim}
EOF
Running the project at this point should result in the following UI:
Data Binding
The data model for this app is simple. We just need a single collection
and a single key/value pair ('result', int) to store the result of the dice
roll.
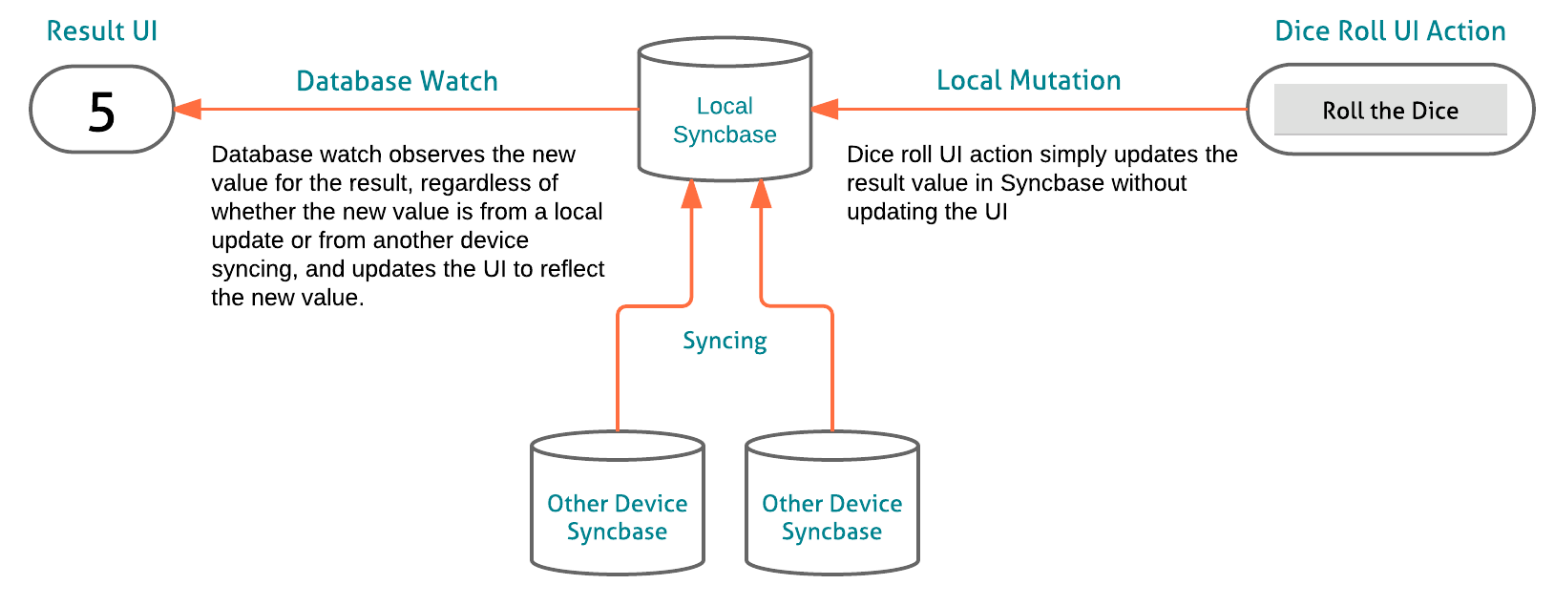
To bind Syncbase data with the UI, we will create a unidirectional data flow using Syncbase's Watch API to handle both local and synced mutation.
With this model, on a dice roll we can change the value in the local Syncbase without updating the UI at all. The local mutation will propagate back through the Watch handler with very low latency enabling us to only update the UI in a single place, regardless of whether the new value is local or was synced from a remote device.
Now let's hook up this model to our code.
cat - <<EOF | sed 's///' > $PROJECT_DIR/app/src/main/java/io/v/syncbase/example/MainActivity.java
{#dim}{#dim-children}package io.v.syncbase.example;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Random;
import io.v.syncbase.Collection;
import io.v.syncbase.Database;
import io.v.syncbase.Syncbase;
import io.v.syncbase.WatchChange;
import io.v.syncbase.exception.SyncbaseException;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "DiceRoller";{/dim-children}{/dim}
private static final String RESULT_KEY = "result";
{#dim}{#dim-children} // Note: Replace CLOUD_NAME and CLOUD_ADMIN with your cloud syncbase name
// and blessing from https://sb-allocator.v.io
private static final String CLOUD_NAME = "<cloud name>";
private static final String CLOUD_ADMIN = "<cloud admin>";
private static final String MOUNT_POINT = "/ns.dev.v.io:8101/tmp/diceroller/users";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
try {
String rootDir = getDir("syncbase", Context.MODE_PRIVATE).getAbsolutePath();
Syncbase.Options options =
Syncbase.Options.cloudBuilder(rootDir, CLOUD_NAME, CLOUD_ADMIN)
.setMountPoint(MOUNT_POINT).build();
Syncbase.init(options);
} catch (SyncbaseException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Syncbase failed to initialize", e);
}
Syncbase.loginAndroid(this, new LoginCallback());
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
Syncbase.shutdown();
super.onDestroy();
}{/dim-children}{/dim}
private class LoginCallback implements Syncbase.LoginCallback {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
Log.i(TAG, "Syncbase is ready");
try {
final Collection userdata = Syncbase.database().getUserdataCollection();
// On dice roll, put a random number into the userdata collection under RESULT_KEY.
final View button = findViewById(R.id.buttonRoll);
if (button == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Resource not found: " + R.id.buttonRoll);
return;
}
button.setEnabled(true);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
private Random random = new Random();
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int randomNumber = random.nextInt(6) + 1;
try {
userdata.put(RESULT_KEY, randomNumber);
} catch (SyncbaseException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "put error", e);
}
}
});
Syncbase.database().addWatchChangeHandler(new Database.WatchChangeHandler() {
@Override
public void onInitialState(Iterator<WatchChange> values) {
onChange(values);
}
@Override
public void onChangeBatch(Iterator<WatchChange> changes) {
onChange(changes);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "watch error", e);
}
private void onChange(Iterator<WatchChange> changes) {
while (changes.hasNext()) {
WatchChange watchChange = changes.next();
Log.i(TAG, "Received watch change: " + watchChange.toString());
if (watchChange.getCollectionId().getName().equals(
Syncbase.USERDATA_NAME) &&
watchChange.getEntityType() == WatchChange.EntityType.ROW &&
watchChange.getChangeType() == WatchChange.ChangeType.PUT &&
watchChange.getRowKey().equals(RESULT_KEY)) {
try {
updateResult(watchChange.getValue(Integer.class));
} catch (SyncbaseException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "watch change error", e);
}
}
}
}
});
} catch (SyncbaseException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Syncbased failed to login", e);
}
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
Log.e(TAG, "LoginCallback: onError", e);
}
}
private void updateResult(int newValue) {
final TextView result = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textViewResult);
result.setText(String.valueOf(newValue));
}
}
EOF
Running The App
To see the data sync between user's devices in a peer-to-peer fashion, we can run the app on two different devices and then turn off Wi-Fi and see it still sync using Bluetooth.
When running the app from Android Studio, you can select multiple devices in
the Select a Deployment Target. If you prefer to use the command line
Multi-Device ADB (madb) is an open-source
tool that makes it easy to run Android apps on multiple devices.
Note
Internet connectivity is required the first time the app is run to authenticate the user and generate an offline auth certificate. Subsequent runs generally do not require Internet connectivity. The auth protocol refreshes its certificate automatically after 12 hours, but the certificate will expire if a device is offline for more than 24 hours.
After running the application on 2 or more devices with Internet connectivity, ensure Bluetooth is enabled on both devices and turn off Wi-Fi, the dice rolls should still sync between the devices just fine!

Want to Dive Deeper?
Checkout the Tutorial to build a full-fledged Todo app and learn more Syncbase features such as sharing, batches and discovery.